In 2025, the way mobile apps are designed and built is changing. Developers aren’t just dragging UI elements into place or writing boilerplate layout code anymore — they’re describing the interface with natural language or sketches, and AI turns that into working UI code.
This evolution is called Generative UI — and it’s transforming the workflows of developers, designers, and product teams across the globe. Especially in tech-forward regions like India and the US, this approach is becoming a competitive advantage.
🎯 What is Generative UI?
Generative UI is the process of using AI (usually large language models or visual models) to generate app interfaces automatically from prompts, examples, voice input, or predefined data. The UI can be produced in the form of:
- Code (React Native, Flutter, SwiftUI, etc.)
- Design components (Figma layouts, auto-styled sections)
- Fully functional prototypes (usable on-device or web)
🧠 Prompt Example:
“Create a fitness dashboard with a greeting message, user avatar, weekly progress bar, and 3 action buttons (Log Workout, Start Timer, Browse Plans).”✅ The AI will then generate production-ready SwiftUI or Flutter code with layout logic, color hints, spacing, and animation triggers.
🛠 Tools Powering Generative UI
Design-Oriented
- Galileo AI: Prompt-driven screen generation with direct export to Flutter, SwiftUI, or HTML.
- Magician (Figma Plugin): Generate copy, layout blocks, and UI flows inside Figma using short prompts.
- Locofy: Convert Figma to React or Flutter code with AI-generated responsiveness hints.
Developer-Oriented
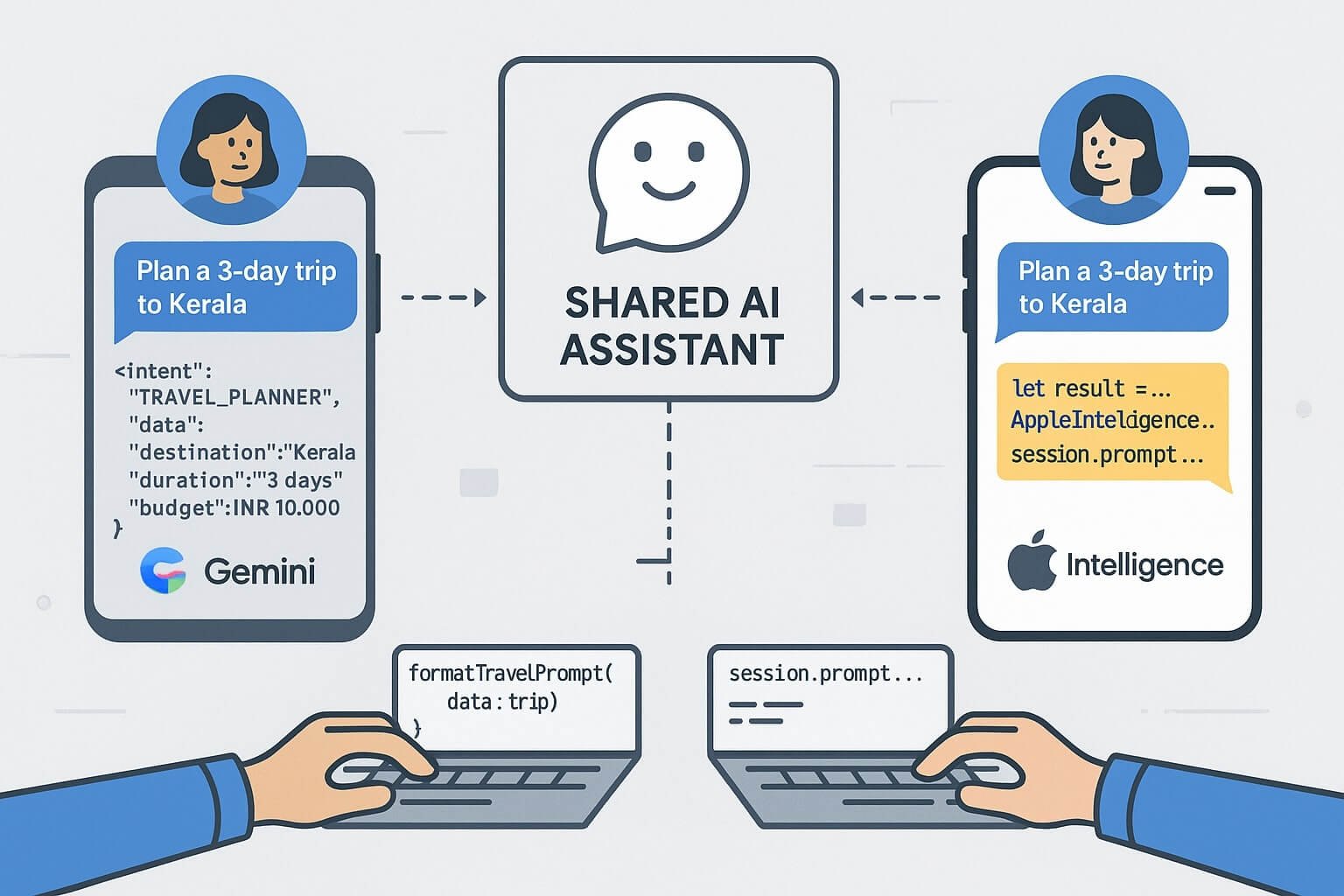
- SwiftUI + Apple Intelligence: Convert voice commands into SwiftUI preview layouts using Apple’s AIEditTask API.
- React GPT-UI Plugin: Use VS Code extension to generate React Native components via prompt chaining.
- Uizard: Turn hand-drawn mockups or screenshots into full working UI code.
🔗 These tools reduce UI dev time by 60–80% depending on complexity — but require review and polish.
🌍 India vs US Adoption
🇮🇳 In India
- Early-stage startups use these tools to rapidly validate MVPs for apps in health, fintech, and social discovery.
- Small dev shops in cities like Hyderabad, Bangalore, and Jaipur use Galileo + Locofy to pitch full app mockups in hours.
- Focus on mobile-first Android deployment — often combining generative UI with Firebase & Razorpay flows.
🇺🇸 In the US
- Product-led teams use these tools to build onboarding flows, test marketing pages, or generate internal tools UI.
- Large companies use AI UI agents as Figma assistants or dev-sideco-pilots.
- Privacy compliance is critical — US teams often use on-premise or custom-trained LLMs for code gen.
⚙️ Generative UI: Technical Workflow Explained
At a high level, the generative UI system follows this architecture:
- Intent Collector: Gathers prompt text, sketch, or config input.
- Prompt Engine: Converts input into structured LLM-friendly instruction.
- LLM Executor: Generates layout tree, styling metadata, or code blocks.
- UI Composer: Maps output to platform-specific elements (e.g. Jetpack Compose, SwiftUI).
- Post Editor: Lets users revise visually or prompt again.
Popular LLMs used include GPT-4 Turbo (via plugins), Claude 3 for interface logic, and OSS models like Mistral for rapid dev pipelines.
🛠 Sample Code: React Component from Prompt
const PromptedCard = () => (
<div className="card-container">
<img src="avatar.png" alt="User Avatar" />
<h3>Welcome Back!</h3>
<button>View Report</button>
<button>New Task</button>
</div>
);
🔁 Prompt Variants & Chaining
- Prompt templates: Generate similar UI layouts for different flows (e.g., dashboard, onboarding, forms).
- Chaining: Add step-by-step instruction prompts for detail control (“Add a dark mode toggle,” “Use neumorphic buttons”).
📐 Design Systems + Generative UI
Integrating AI with design systems ensures consistency. Prompts can invoke style tokens (color, spacing, radius, elevation) dynamically.
- Token Reference: Instead of using hex values, prompts like “Use primary button style” will fetch from Figma/Style Dictionary.
- Dynamic Scaling: LLMs now understand layout responsiveness rules.
Code: Flutter Button from Tokenized Prompt
ElevatedButton(
style: ButtonStyle(
backgroundColor: MaterialStateProperty.all(AppTheme.primaryColor),
elevation: MaterialStateProperty.all(3),
),
onPressed: () {},
child: Text("Start Workout"),
)
🎯 Use Cases for Generative UI in 2025
- Onboarding Screens: Generate personal walkthroughs per feature release
- Admin Dashboards: Create custom data views using query-driven prompts
- Marketing Sites: AI builds tailored pages for each traffic segment
- Creator Apps: No-code layout generation for event flows or quizzes
📊 Versioning + Collaboration with AI UI
Devs now use tools like PromptLayer or Galileo History to track prompt → output version chains, enabling collaboration across QA, design, and PMs.
Prompt diffs are used the way Git diffs are — they compare new layouts to previous designs, highlighting what AI changed.
🧪 Testing AI-Generated Interfaces
- Visual Regression: Screenshot diffing across resolutions
- Interaction Testing: Use Playwright + AI traces
- Accessibility: Run aXe audit or Apple VoiceOver audit
⚠️ Limitations of Generative UI (and How to Handle Them)
Generative UI isn’t perfect. Developers and designers should be aware of these common pitfalls:
- Inconsistent layout logic: AI might generate overlapping or misaligned components on edge cases.
- Accessibility blind spots: AI tools often ignore color contrast or keyboard navigation if not prompted explicitly.
- Platform mismatches: Flutter code from AI might use native gestures incorrectly; SwiftUI output might skip platform-specific modifiers.
- Performance issues: Excessive DOM nesting or widget trees can slow rendering.
🧩 Mitigation Strategies
- Use linting + component snapshot testing post-generation
- Prompt clearly with sizing, layout type, and device constraints
- Include accessibility expectations in the prompt (e.g. “Include screen reader support”)
- Use AI as a first-pass generator, not final implementation
🧠 Developer Skills Needed for 2025
As AI becomes a part of UI workflows, developers need to evolve their skills:
- Prompt writing + tuning — understanding how phrasing impacts output
- LLM evaluation — measuring UI quality across variants
- Design token management — mapping outputs to system constraints
- AI-aided testing — writing tests around generated code
- Toolchain integration — working across AI APIs, design tools, and CI systems
📈 Market Outlook: Where This Trend Is Going
Generative UI is not a temporary trend — it’s a shift in how user interfaces will be created for mobile apps, web, AR/VR, and embedded platforms.
🔮 Predictions
- Apple and Google will integrate prompt-based layout tools in Xcode and Android Studio natively
- LLMs will generate UI with personalization and accessibility baked in
- Multi-modal inputs (voice, sketch, pointer) will merge into a single design-to-code pipeline
- More developers will work alongside AI agents as co-creators, not just co-pilots
By 2026, app teams may have an “LLM Specialist” who curates prompt libraries, maintains UI generation templates, and reviews layout suggestions just like a design lead.